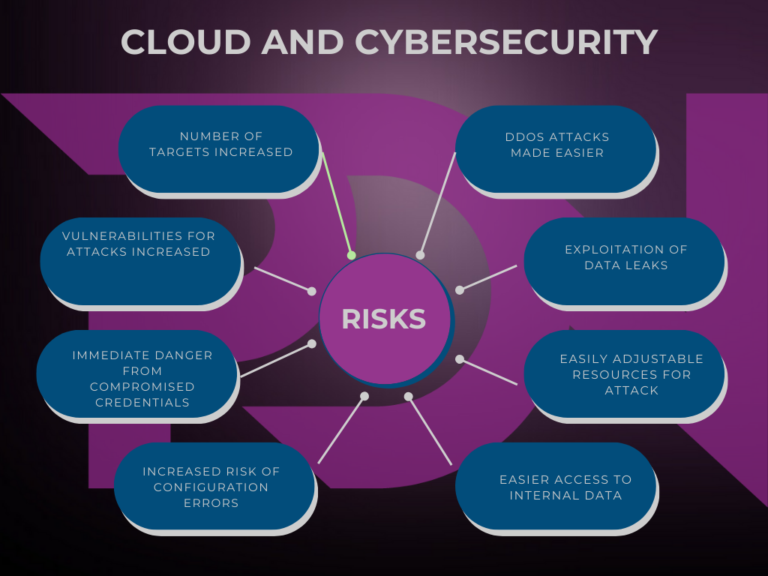
But, of course, this accessibility of data on the Internet inevitably increases cybersecurity risks. What are they?
Increased number of potential targets
Cloud computing has enabled companies to store and manage huge amounts of data and applications in cloud infrastructures. This has created new potential targets for attackers, as much sensitive data is now accessible via the Internet.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks
Cloud services can be used to launch massive DDoS attacks using the computing and storage power available. Hackers can also rent cloud resources to amplify their attacks and disrupt online services.
Data leakage
Misconfigurations in the cloud, such as mismanaged permissions, have led to numerous data leaks. Attackers exploit these vulnerabilities to gain access to sensitive data stored in the cloud.
Scalable computing resources
Cloud infrastructures offer the possibility of rapidly adjusting computing resources in line with demand. This means that attackers can also use these capabilities to execute massive attacks without the need for their own expensive infrastructure.
Internal threats
Cloud service providers have privileged access to their customers’ data. This creates a potential risk of internal breach of trust or compromise. Hackers could attempt to infiltrate cloud support teams to gain access to data.
Configuration-dependent security
Security in the cloud depends largely on how services are configured and managed. Configuration errors can inadvertently expose sensitive data, and attackers actively seek out such vulnerabilities.
Malicious cryptomining
Attackers often use stolen cloud resources to mine crypto-currencies, which can be difficult for resource owners to detect.
Cloud storage services
Cloud storage services are often used to store sensitive data, and if login credentials are compromised, data can be stolen or ransomware deployed.
Network traffic analysis
Cloud services offer advanced analysis capabilities. Attackers can use these capabilities to analyze network traffic and identify potential vulnerabilities.
The cloud has indeed created new opportunities for attackers, introducing additional security challenges. Companies therefore need to invest in robust security practices to minimize the risks associated with those cyber-security risks in a cloud environment.