In the first part of our article, we looked at what the darkweb is and what it is used for, but what role does it play in the spread of piracy? That’s what we’re going to try to find out today. Since you can literally buy and sell anything on the dark web, it obviously also serves as a market for piracy tools and services. For example, you can buy malware kits, exploit security holes and even rent botnets to carry out DDoS attacks.
One of the main attractions of the Dark Web is its infrastructure, which is designed to guarantee anonymity. Hackers can operate without fear of being easily identified. IP addresses are masked and communications encrypted using protocols such as Tor, making the work of law enforcement agencies considerably more difficult. Anonymity encourages criminal activity and allows hackers to exchange information or sell stolen data without the risk of revealing their identity.
As we have already written, the Dark Web is well known for hosting numerous underground marketplaces where hacking tools and services are for sale.
For example, Exploit Kits, which contain software to exploit security vulnerabilities in systems, are readily available for payment in cryptocurrencies. These kits enable people without advanced technical skills to carry out sophisticated cyber attacks.
In addition, on-demand hacking and piracy services are available. Cybercriminals offer to hack into online accounts, steal data or carry out attacks against companies on behalf of anonymous customers.
Hacker forums and communities, where information is exchanged, hacking techniques are shared, and ‘training’ is offered to newcomers, are also available on the darkweb. This creates an environment where hacking becomes more accessible, even for those without in-depth technical skills.
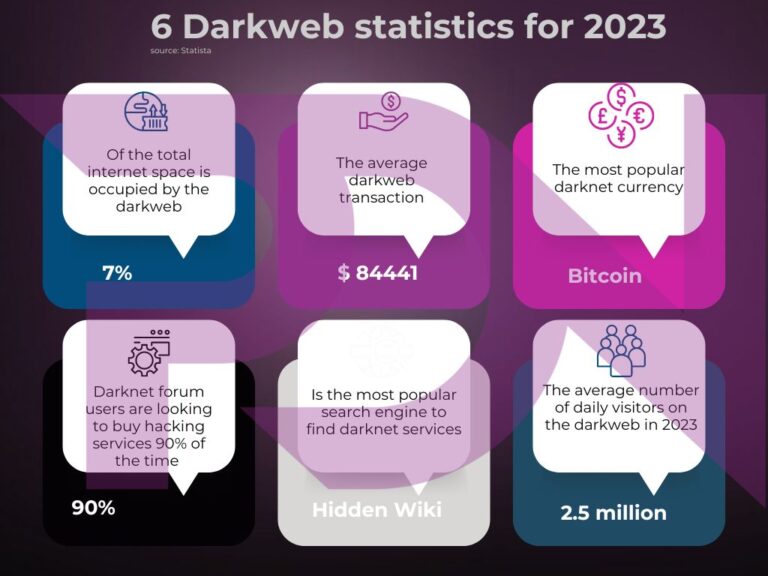
This particular environment has consequences for businesses, individuals and even governments.
One of the Dark Web’s most significant result is the massive proliferation of stolen data, particularly company databases. When a company or online service is hacked, the stolen personal information (such as names, email addresses, phone numbers, passwords, and sometimes even financial information) often ends up on the Dark Web. These databases are then offered for sale, and buyers can use this information to commit other crimes, such as identity theft or financial fraud.
Hackers also exploit this data for massive phishing campaigns, where fraudulent emails are sent to victims to trick them into providing even more sensitive information, or to infect their devices with malicious software.
Data theft through leaks and hacks also has devastating consequences for individuals. Once on the Dark Web, personal information can be exploited to commit large-scale fraud, such as opening bank accounts under false identities or making fraudulent online purchases. Individual victims of such hacking often face significant complications in restoring their identity, finances and reputation. Cybercriminals also target individuals directly with phishing attacks or digital harassment.
Finally, the Dark Web is playing a crucial role in the escalation of state-sponsored cyber attacks. Increasingly, nation states are turning to cyber espionage and digital attacks to obtain sensitive information about other governments or strategic companies.
The Dark Web has also created a veritable stolen data economy. The illegal trade in this information is organised around anonymous sales platforms, where prices vary according to the quality and quantity of the data on offer. For example, credit card numbers, PayPal account identifiers and passport details are traded at very high prices, making this a very lucrative sector for cybercriminals.
Companies are the main targets of hackers operating on the Dark Web. Cybercriminals exploit system vulnerabilities to steal sensitive data. Ransomware attacks have become commonplace.
The economic repercussions of such attacks are enormous. Companies often have to pay ransoms, repair damaged systems, and face legal or public relations costs to restore customer confidence. by 2021. This trend is only set to increase as a result of activities facilitated by the Dark Web.

Governments and security agencies around the world are working hard to combat criminal activity on the Dark Web. Operations such as Operation Onymous, led by Europol and the FBI in 2014 have resulted in the closure of several illegal marketplaces and the arrest of their administrators. However, despite these efforts, the decentralised and anonymous nature of the Dark Web makes these operations complex and the results often temporary. Since then, no large-scale operations have taken place for this reason.
Given the increase in cyber-attacks, cyber-security has become a booming sector. Companies are investing massively in protection solutions such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems and vulnerability management programmes. Cybersecurity professionals are at the forefront of countering cybercriminals, thwarting hacking attempts and strengthening digital defence systems.
Advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning are used to detect and neutralise threats in real time. In addition, practices such as cyber hygiene, where employees are trained to identify phishing attempts or to use secure passwords, help to strengthen defences against hacking.
Governments are passing more and more laws to combat cybercrime. For example, the European Union has introduced the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which imposes severe penalties for leaking personal data. In the United States, laws such as the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act make it possible to prosecute cyber criminals.
However, regulating the Dark Web and is a difficult task. The cross-border nature of these crimes complicates coordination between the various national authorities, while the anonymity of the criminals makes them difficult to identify and arrest.
The Dark Web and digital piracy will continue to evolve as technology advances. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are already being used to improve hacking and piracy techniques, but also to strengthen digital defences. The development of blockchain and cryptocurrencies offers new opportunities for criminals while providing new ways of tracking down illicit transactions.
Come back for our series about blockchain in November. In the meantime, if you have a film, series, software or e-book to protect, don’t hesitate to call on our services by contacting one of our account managers; PDN has been a pioneer in cybersecurity and anti-piracy for over ten years, and we’re bound to have a solution to help you. Happy reading and see you soon!
Share this article