The Dark Web is one of those terms that everyone has heard of, but few know how to define. Associated with a variety of clandestine activities, from the exchange of stolen data to the sale of illegal products, the Dark Web is a place where digital piracy proliferates. October’s theme allows us to dive into this universe to discover what exactly the Dark Web is, and to explore dark web practices associated with piracy.
To understand what the Dark Web is, it’s first essential to differentiate between the different strata of the Internet.
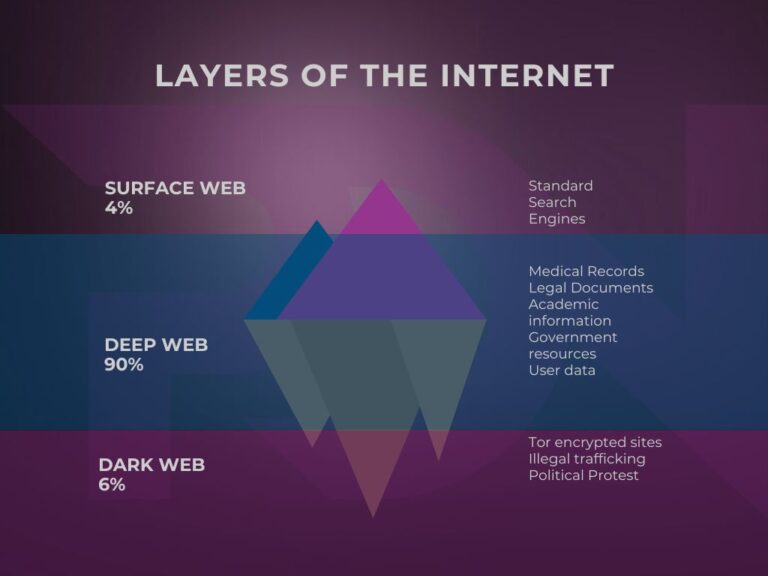
The Surface Web is the set of websites indexed by search engines such as Google, Bing or Yahoo. This is what the average user accesses when surfing the Internet. Content is public, easily accessible and regulated by local and international laws.
Below the surface of the web lies the Deep Web, which includes all sites and databases not indexed by search engines. This is not necessarily an area for criminals; it includes medical data, scientific databases, corporate intranets and so on. These sites often require specific authentication to access them. This space represents an important part of the Internet.
This is a subsection of the deep web. To access it, you’ll need specific tools. Unlike the deep web, which is often harmless, the dark web is reputed to host illicit activities, although it is also used by journalists, political dissidents and activists wishing to protect their identity. Despite these legitimate uses, in this article we’ll focus on the part of the dark web that serves as a platform for illegal activities.
To access the dark web, users have to use special software to mask their identity and location. The most famous of these is Tor (The Onion Router). Tor is a decentralized network that enables anonymous browsing by encrypting and redirecting Internet traffic through several relays spread around the world.
The Tor principle is based on onion routing. Internet traffic is encrypted and sent through several layers of relays (or nodes). Each node knows only the packet’s immediate origin and destination, but never its entire path. This makes it extremely difficult to trace the exact identity or location of the user. Everyone’s anonymity is perfectly preserved.
Sites accessible via Tor have addresses ending in “.onion”, and can only be consulted by Tor-compatible browsers.
In addition to Tor, there are other networks used to access the dark web, such as I2P (Invisible Internet Project) or Freenet. These networks operate on similar principles in terms of privacy and anonymity, although Tor is the most widely used to access dark web sites.

Much of the attention on the dark web is linked to its black markets. One of the most famous was Silk Road. The site is now closed, but it enabled people to buy drugs online, as well as other illegal trading sites. These platforms enabled the anonymous purchase of prohibited goods or services, including drugs, firearms, pirated data or malware.
Cryptocurrencies, in particular Bitcoin, are often used for these transactions due to their relative anonymity. Bitcoin enables money to be transferred without going through traditional banking channels, offering a degree of financial invisibility, allowing hackers to receive payments almost anonymously, complicating investigations into the tracking of funds. Although some initiatives have been launched to monitor cryptocurrency transactions, criminals are often one step ahead of the authorities.
Visit us again in mid-October for the continuation of our article on the darkweb. In the meantime, if you have a film, series, software or e-book to protect, don’t hesitate to call on our services by contacting one of our account managers; PDN has been a pioneer in cybersecurity and anti-piracy for over ten years, and we’re bound to have a solution to help you. Happy reading and see you soon!
Share this article